Which Countries Speak French In Africa: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the French language's influence in Africa is essential for anyone interested in the continent's cultural and historical dynamics. French is one of the most widely spoken languages in Africa, serving as an official or co-official language in numerous countries. This article explores the countries in Africa where French is predominantly spoken, the historical context behind its spread, and its significance in contemporary society.
In Africa, French is not just a language; it is a means of communication that bridges various ethnic groups and cultures. The legacy of colonialism, along with the ongoing political and economic ties to France, has played a significant role in the prominence of the French language across the continent. By examining the countries where French is spoken, readers can gain insights into the shared heritage and the unique identity of these nations.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various countries in Africa that speak French, providing valuable information about their demographics, culture, and the role of the French language in their societies. Whether you are a language enthusiast, a traveler, or simply curious about Africa, this article is designed to provide you with a thorough understanding of the linguistic landscape of French-speaking countries in Africa.
Table of Contents
- Historical Context of French in Africa
- List of Countries That Speak French in Africa
- Demographics and Statistics
- The Role of French in African Societies
- Cultural Impacts of the French Language
- French in Education Systems
- Economic Importance of French
- The Future of the French Language in Africa
Historical Context of French in Africa
The introduction of the French language in Africa can be traced back to the colonial period, when France established colonies in various parts of the continent. Countries such as Senegal, Ivory Coast, and Madagascar were among the first to experience French colonial rule, leading to the establishment of French as the language of administration, education, and governance.
As a result of colonization, the French language became intertwined with the political and social frameworks of these nations. Even after gaining independence, many former colonies retained French as an official language due to its status and the practical benefits of maintaining ties with French-speaking countries.
Today, French is not only a remnant of colonial history but also a vital part of national identity in many African countries. It serves as a lingua franca that facilitates communication among diverse ethnic groups.
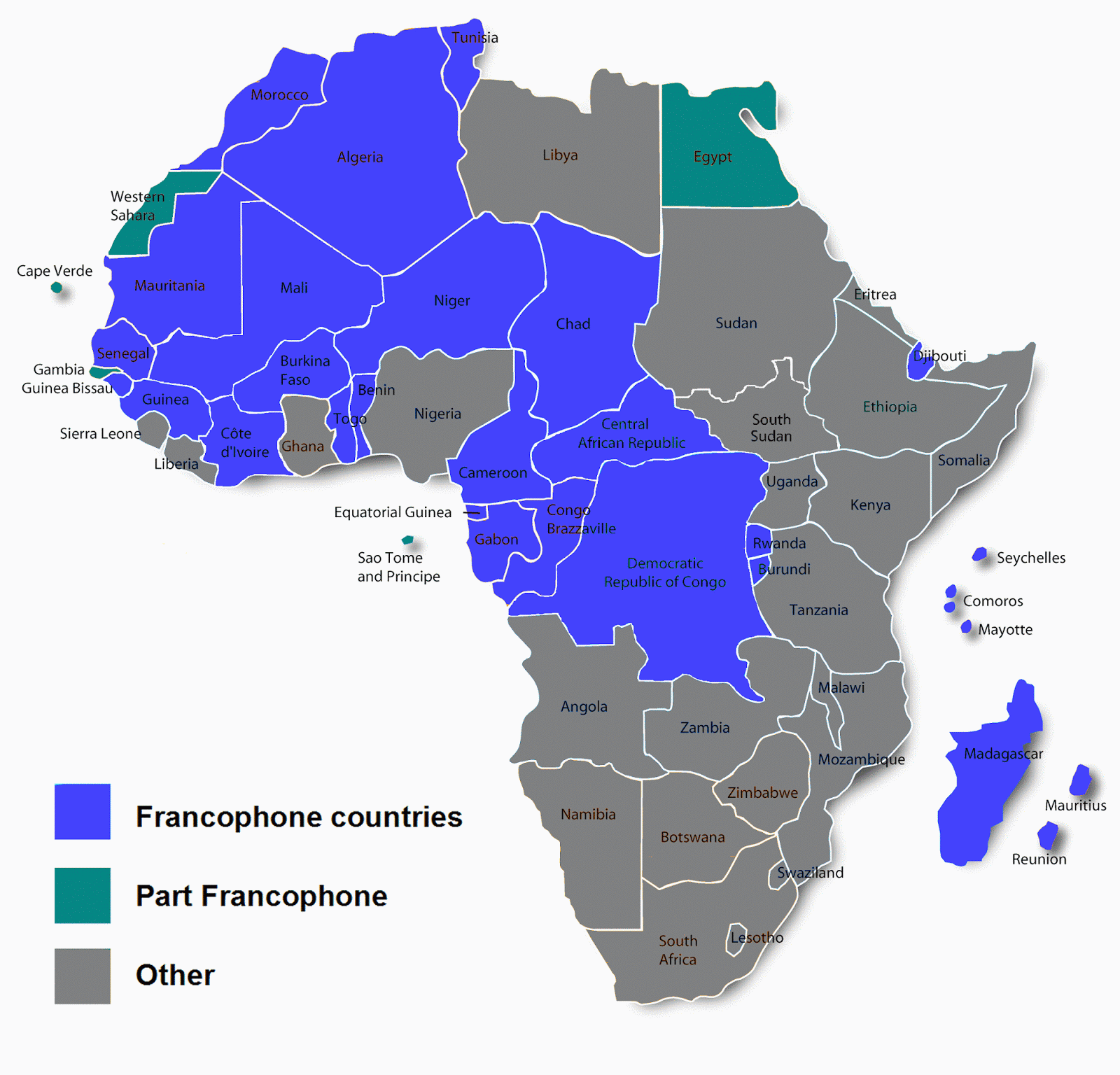
List of Countries That Speak French in Africa
Here is a list of African countries where French is an official or widely spoken language:
- Algeria
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cabo Verde
- Cameroon
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Congo, Republic of the
- Congo, Democratic Republic of the
- Djibouti
- Equatorial Guinea
- France
- Gabon
- Guinea
- Ivory Coast
- Madagascar
- Mali
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Togo
- Tunisia
Table of French-Speaking Countries
| Country | Official Status | Estimated French Speakers |
|---|---|---|
| Algeria | Official | Over 10 million |
| Cameroon | Official | About 6 million |
| Ivory Coast | Official | Over 25 million |
| Senegal | Official | About 15 million |
| Madagascar | Co-official | Over 8 million |
Demographics and Statistics
According to estimates, around 120 million people in Africa speak French, making it one of the most widely spoken languages on the continent. The demographic distribution of French speakers varies significantly between urban and rural areas, with urban centers often showcasing a higher proficiency in French due to better access to education and media.
In countries like Senegal and Ivory Coast, French is often used in formal settings, while local languages are preferred in everyday conversations. This linguistic duality reflects the rich cultural tapestry of Africa.
Moreover, the demographic makeup of French speakers is diverse, including various ethnic groups, each contributing to the unique ways in which French is spoken across the continent.
The Role of French in African Societies
French plays a crucial role in various aspects of African societies, including:
- Administration: French is the primary language of government and legal proceedings in many countries.
- Education: The language is often used as the medium of instruction in schools and universities, influencing the educational landscape.
- Media: French-language media, including television, radio, and print, are prevalent and contribute to the dissemination of information.
Cultural Impacts of the French Language
The French language has significantly influenced African literature, music, and art. Notable authors, such as Léopold Sédar Senghor and Aime Césaire, have contributed to the richness of Francophone literature. Additionally, music genres like rap and hip-hop often incorporate French lyrics, showcasing the language's adaptability and relevance in contemporary culture.
French cultural institutions, such as the Alliance Française, play a vital role in promoting French culture and language through various artistic and educational programs across Africa.
French in Education Systems
In many African countries, French is the language of instruction in primary, secondary, and tertiary education. This practice has both advantages and challenges:
- Advantages:
- Access to a broader range of educational resources and literature.
- Better opportunities for higher education and employment in French-speaking countries.
- Challenges:
- Language barriers for students who are more proficient in local languages.
- Unequal access to quality education in French-speaking institutions.
Economic Importance of French
The proficiency in French opens up numerous economic opportunities for individuals and businesses in Africa. As many African countries engage in trade with France and other Francophone nations, the ability to communicate in French is an asset in various sectors, including:
- Tourism: French-speaking guides and services attract tourists from Francophone countries.
- Business: French is often used in negotiations and contracts with international partners.
- Diplomacy: French is one of the official languages of many international organizations, making it essential for diplomatic relations.
The Future of the French Language in Africa
The future of the French language in Africa appears promising, with projections indicating that the number of French speakers in Africa will continue to grow. This growth is attributed to:
- The increasing population of French-speaking youth.
- The expansion of educational institutions teaching French.
- The strengthening of economic ties between African countries and Francophone nations.
However, challenges remain, including the need to balance the use of French with the preservation of local languages and cultures. Efforts to promote multilingualism are crucial to ensure that the rich linguistic diversity of Africa is maintained
Happy Birthday Sister In Law: Celebrating Family Bonds And Special Moments
Car Wash In Kenya: Your Ultimate Guide To Keeping Your Vehicle Spotless
Canada Rap: Exploring The Vibrant Hip-Hop Scene In The Great White North